Describe the Biological Basis for Parkinson's Disease
A woman notices that her father has started to move his fingers in such a way that it looks like he is rolling something despite nothing actually being there. Parkinsons is characterized by inability to initiate movements.
The Neurochemistry Of Parkinson S Disease Proteintech Group
Parkinsons illness is a cerebrum issue that prompts shaking firmness and difficulty with strolling equilibrium and coordination.

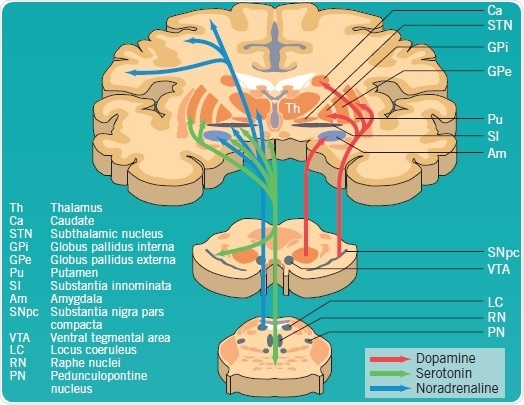
. The Nigrostriatal pathway carries dopamine from the substantia nigra to the striatum which is crucial for instrumental learning of complex motor sequences via long term potentiation. LRRK2 has been proposed to function in membrane trafficking 3 and colocalizes with microtubules 4. Include specific molecules and cells involved in the pathogenesis of po.
Since it mostly affects people 60 and older your risk goes up as the years go by. If your parent brother or sister has. Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body.
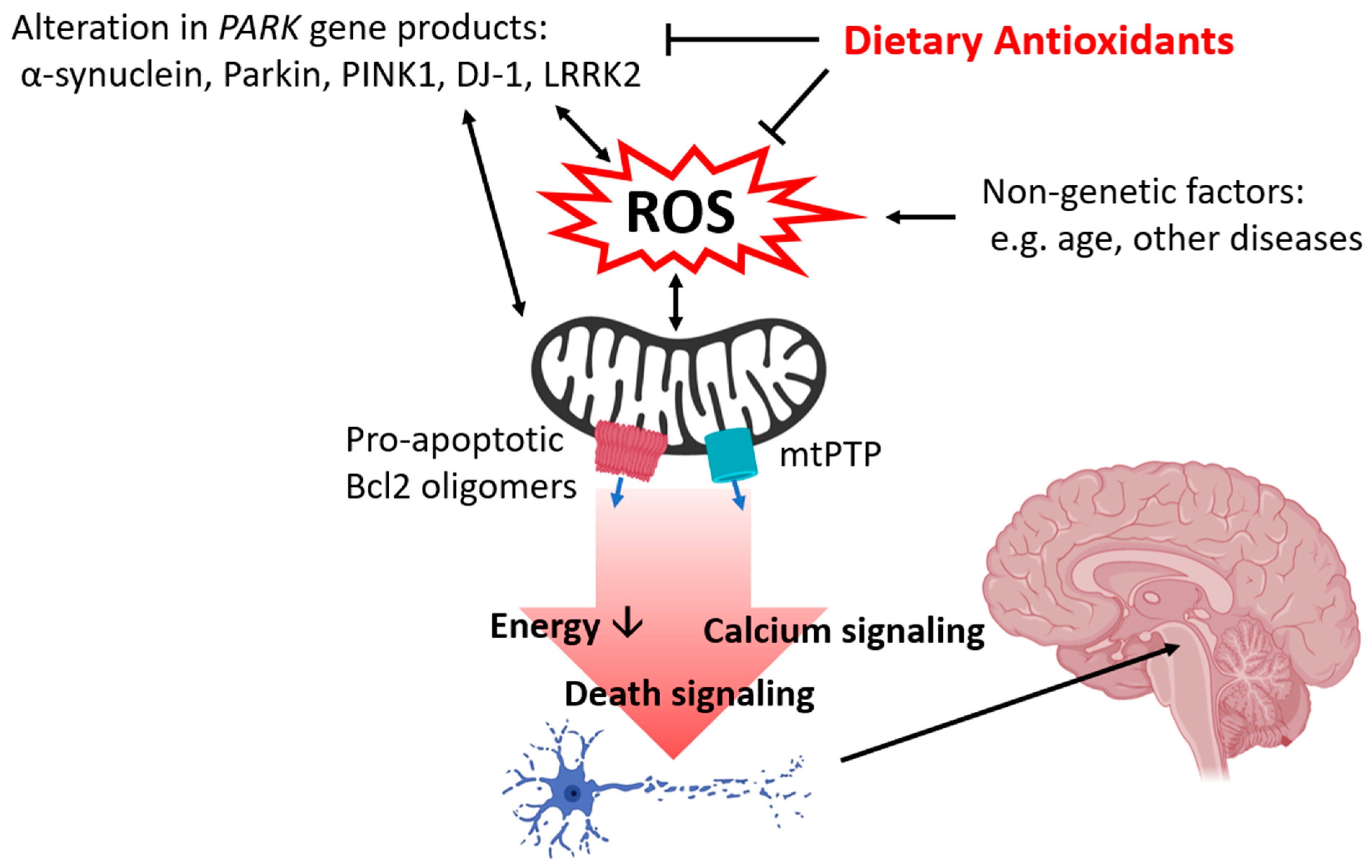
A molecule that can cause damage to brain cells is alpha-synuclein that build up and form Lewy bodies that can damage neurons. Parkinson disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain. Nevertheless several clinical issues cannot be.
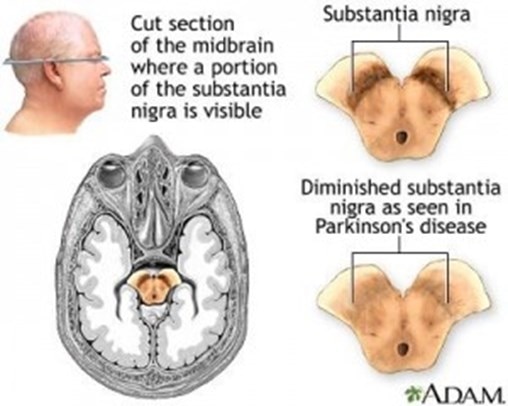
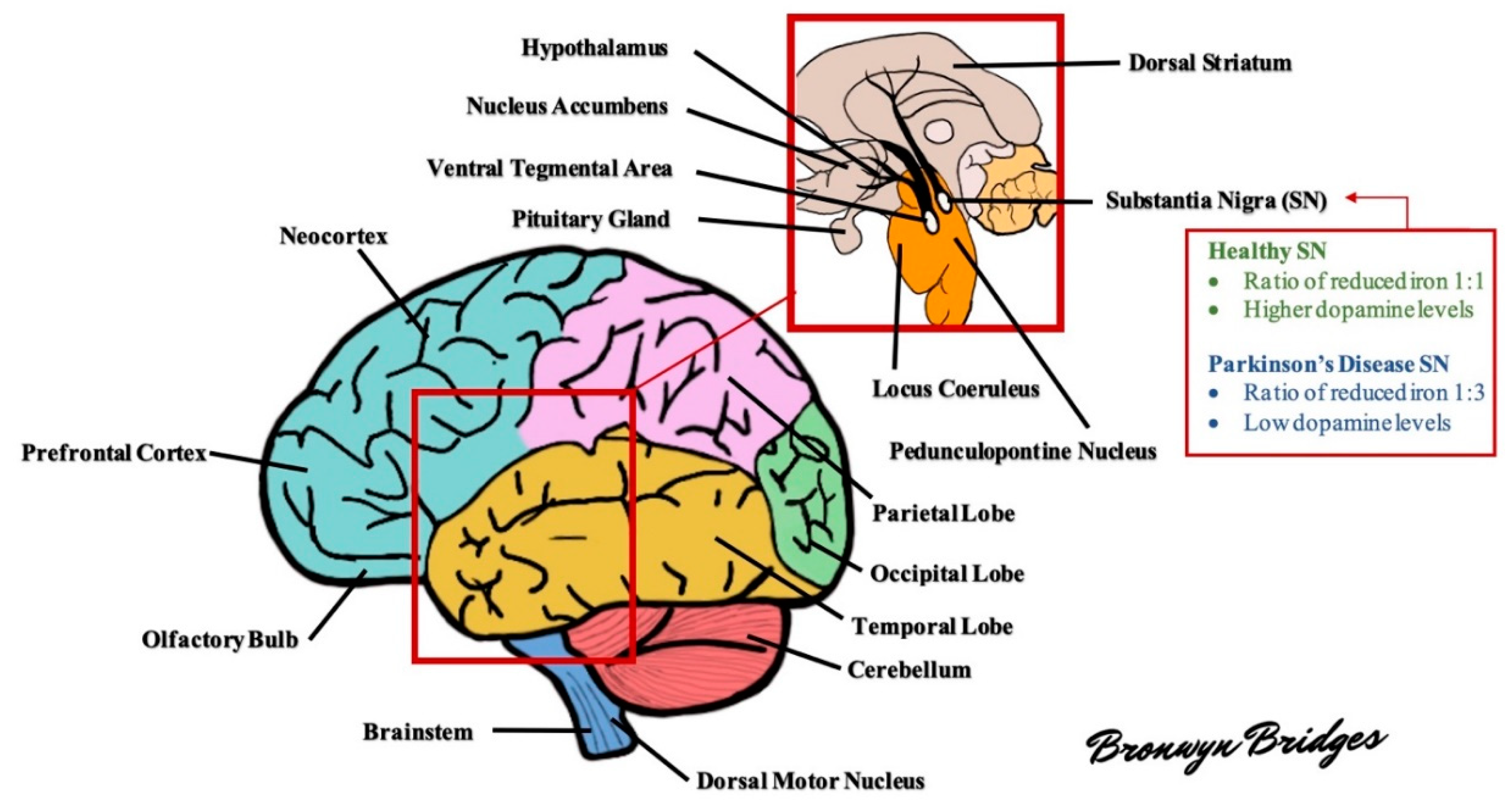
Parkinsons disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. It happens when cells that produce dopamine die in the brain. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopaminergic neurons from Substantia nigra pars compacta degenerate. Alex skim through those articles and see if there is any useful information abour a link between caffeine and Parkinsons Disease while I call Granddad added Sally. 1 The pathologic changes in PD occur gradually and progressively over many years with a.
Parkinsons indications ordinarily start step by step and deteriorate over the long haul. Parkinsons disease PD which afflicts nearly 1 of the population above the age of 60 is a multisystem neurodegenerative disorder in which progressive loss of midbrain dopamine DA neurons with resulting dopaminergic deafferentation of the basal ganglia gives rise to characteristic motor disturbances that include slowing of movement muscular rigidity and. We do not know exactly what causes Parkinsons disease PD but scientists believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors are the cause.
Describe the biological basis for Parkinsons Disease PD. As the disease progresses people may have difficulty walking and talking. Dopamine sends signals to co-ordinate body movements.
The striatum composed of the caudate and putamen is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 LRRK2 is the most commonly mutated gene in familial Parkinsons disease 1 and is also linked to its idiopathic form 2. On this ground several cellular and animal models have been developed to investigate disease etiology and pathogenetic mechanisms.
Human herpesvirus 6 and HHV-7 have long been thought to play a role in this disease but there was hardly any causative mechanism known. Describe any side effects and adverse effects of the drug treatment and their biological basis including issues related to contraindications interactions drug metabolism and elimination. In addition explain risks benefits and ethical implications for high-risk and exceptional treatment conditions.
Ad Learn More About The Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease That Can Help You. Causes Symptoms and Treatments. Learn all of the important facts about Parkinsons disease including treatment.
Although it is mostly a sporadic disorder 1530 of all cases are linked to a genetic background. Researchers do not know why some people develop Parkinsons and others do not. The extent to which each factor is involved varies from person to person.
Parkinsons disease PD is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing dopaminergic neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra. Parkinsons disease is the most common neurodegenerative movement disorder. Parkinson s Disease PD is caused by the loss of nerves cells in the substantia nigra part of the brain that produces dopamine.
Parkinsons Disease is caused by a metabolic error. The lack of dopamine prevents the disinhibition of the thalamus reducing voluntary movement. Despite the fundamental importance of LRRK2 for understanding and treating Parkinsons disease structural information on the.
Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. Symptoms generally develop slowly over years. Genetics cause about 10 to 15 of all Parkinsons.
Parkinsons disease symptoms mainly result from low or falling levels of dopamine a neurotransmitter. This indicates that the basal ganglia is important in the initiation of movement. The neurobiological basis for Parkinsons disease PD is degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons and the pathological deposition of the protein α-synuclein in intraneuronal Lewy inclusions within vulnerable populations of neurons in the brain Figure 1A-D.
The degeneration of neurons in the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway is responsible for the effects of Parkinsons disease. The progression of symptoms is often a bit different from one person to another due to the diversity of the disease. Parkinsons disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements such as shaking stiffness and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Parkinsons disease is associated with cell death within the substantia nigra a structure of the midbrain.
Neurobiology And Therapeutic Targets Of Parkinson S Disease

Parkinson S Disease A Closer Look At Stem Cells
Antioxidants Free Full Text Dietary Antioxidants And Parkinson S Disease Html
Molecules Free Full Text The Pathology Of Parkinson S Disease And Potential Benefit Of Dietary Polyphenols Html
Comments
Post a Comment